1.Research Summary
The field of ophthalmology and visual sciences is classified into clinical groups designated glaucoma, retina and vitreous body, neurophthalmology/strabismic amblyopia, cornea/infection, and ophthalmic tumor/ophthalmic plastic, and highly-specialized research is conducted in each area.
2.Research Groups
3-1.Glaucoma Group
Research subjects
Changes in axonal transport deficits and properties of the cribrosa lamina
that occur in the optic disc in glaucoma
Research on morphological defects of the axonal mitochondria in the optic
disc in glaucoma
Analysis of the classification of disease types and phenotypes according
to genes related to primary open-angle glaucoma, and development of therapies
Detection and analysis of changes in the cribrosa lamina in glaucoma using
optical coherence tomography (OCT)
Long-term follow-up analysis and prognostic prediction of primary open-angle
glaucoma using an automated perimeter
Prediction of progression based on analysis of the correlation between
visual field (function) and OCT findings (morphology) in glaucoma
Relationship between visual field and QOL (Quality of life) in glaucoma,
especially driving and reading
Analysis of the clinical conditions of primary angle-closure/ glaucoma,
relationship with corneal endothelial damage
3-2.Retina and Vitreous Body Group
Research subjects
Research on the effect of vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGFs) on
glaucoma angiogenesis
Research on the therapeutic efficacy of anti-VEGF drugs for age-related
macular degeneration
Research on the clinical conditions of central serous chorioretinopathy
Development of new surgical procedures and equipment
3-3.Neurophthalmology Group
Research subjects
Clarification of the clinical conditions for treatment of anti-aquaporin
4 antibody-positive optic neuritis
Development of new imaging diagnostics for optic nerve disease
Evaluation of transcorneal electrical stimulation treatment for optic nerve
diseases
3-4.Strabismic Amblyopia Group
Research subjects
Changes in the cerebral cortex ultrastructure in amblyopia
Clarification of clinical conditions for the treatment of specific types
of accommodative esotropia
3-5.Cornea/Infection Group
Research subjects
Research on epidemiological studies on uveitis
Research on the therapeutic efficacy of biological products for uveitis
Research on surgical results of corneal transplantation
3-6.Ophthalmic Tumor/Ophthalmic Plastic Group
Research subjects
Research on the development of BRAF (V600E) in ocular malignant melanoma
Research on serological and histopathological examinations of patients
with ocular lymphoproliferative diseases and malignant lymphoma meeting
the diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related disease
4.Research Results
[Area] Ophthalmology and visual sciences (glaucoma)
[Research subject]
Research on morphological defects of the axonal mitochondria in the optic disc in experimental glaucoma
[Description]
India ink was injected into the rat anterior chamber, and at the time when
carbon particles were accumulated in the trabecular meshwork, a model of
chronic ocular hypertension (1-3 M) was induced by argon laser coagulation
which was repeated a few times. Microscopy revealed thinning of the neural
retina and backward bending of the laminar beam. On electron microscopic
examination of the axon adjacent to the optic disc, among normal mitochondria,
there were alterations including giant and swollen mitochondria, as well
as crystalline inclusions while the double membrane structure was maintained.
In the rat model of acute ocular hypertension, caspase 3 activation increased
in the retinal ganglion cell layer on Day 1 after ocular pressure increased.
On Day 3, TUNEL-positive cells were expressed in the retinal ganglion cell
layer. On Day 7, 50% were positive. It was suggested that an execution
mechanism by which axonal transport deficits followed by apoptotic retinal
ganglion cell death via abnormal mitochondrial function might be involved
in optic nerve damage from glaucoma.
[Photographs]
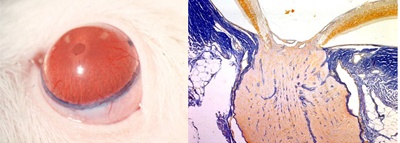
Creation of a rat glaucoma model (microscopy)
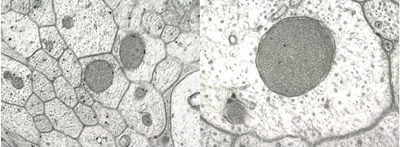
Altered mitochondria scattered in the axon (electron microscopy)
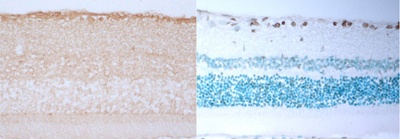
Immunostaining of Caspase 3 in retinal tissue, TUNEL staining finding
[Area] Ophthalmology and visual sciences (neurophthalmology/strabismic amblyopia)
[Research subject]
Clarification of clinical conditions for the treatment of anti-aquaporin 4 antibody-positive optic neuritis
[Description]
In patients with anti-aquaporin 4 antibody-positive optic neuritis, the
visual acuity prognosis is poor, and this disease frequently recurs; thus,
appropriate therapies for improving visual acuity and preventing recurrence
need to be considered. We evaluated the course of visual performance after
the treatment of anti-aquaporin 4 antibody-positive optic neuritis in collaboration
with multiple institutions in Japan. Steroid pulse therapy alone has been
shown to improve corrected visual acuity by at least 0.5 3 months after
the start of therapy in approximately 44% of patients, but the course of
visual acuity was poor in remaining patients. This research provided important
evidence on the course of visual performance as the first step for the
treatment of anti-aquaporin 4 antibody-positive optic neuritis.
[Photographs]
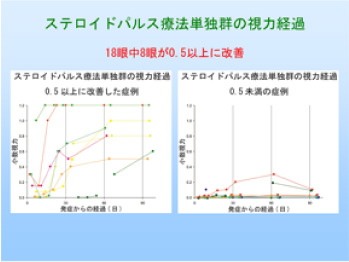
[Area] Ophthalmology and visual sciences (ophthalmic tumor/ophthalmic plastic)
[Research subject]
Research on the development of BRAF (V600E) in ocular malignant melanoma
[Description]
For some types of tumors such as primary cutaneous malignant melanoma,
colorectal cancer and hairy cell leukemia, oncogenic mutations of BRAF
occur. In tumors with BRAF mutations, mitogen-activated protein kinase
pathway activation increases, and susceptibility to BRAF and MEK (mitogen-activated
or extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase) inhibitors increases.
The frequency of BRAF mutations in ocular malignant melanoma will be investigated
by our group.
Please see the Ophthalmology website for a detailed description of our research.
