Ophthalmology
HOME > Activities > Clinical Medicine > Ophthalmology
1.Research Summary
The field of ophthalmology and visual sciences is classified into clinical groups designated glaucoma, retina and vitreous body, neurophthalmology/strabismic amblyopia, cornea/infection, and ophthalmic tumor/ophthalmic plastic, and highly-specialized research is conducted in each area.
2.Research Groups
- Glaucoma Group
- Retina and Vitreous Body Group
- Neurophthalmology Group
- Strabismic Amblyopia Group
- Cornea/ Infection Group
- Ophthalmic Tumor/Ophthalmic Plastic Group
3-1.Glaucoma Group
Research subjects
Changes in axonal transport deficits and properties of the cribrosa lamina
that occur in the optic disc in glaucoma
Research on morphological defects of the axonal mitochondria in the optic
disc in glaucoma
Analysis of the classification of disease types and phenotypes according
to genes related to primary open-angle glaucoma, and development of therapies
Detection and analysis of changes in the cribrosa lamina in glaucoma using
optical coherence tomography (OCT)
Long-term follow-up analysis and prognostic prediction of primary open-angle
glaucoma using an automated perimeter
Prediction of progression based on analysis of the correlation between
visual field (function) and OCT findings (morphology) in glaucoma
Relationship between visual field and QOL (Quality of life) in glaucoma,
especially driving and reading
Analysis of the clinical conditions of primary angle-closure/ glaucoma,
relationship with corneal endothelial damage
3-2.Retina and Vitreous Body Group
Research subjects
Research on the effect of vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGFs) on
glaucoma angiogenesis
Research on the therapeutic efficacy of anti-VEGF drugs for age-related
macular degeneration
Research on the clinical conditions of central serous chorioretinopathy
Development of new surgical procedures and equipment
3-3.Neurophthalmology Group
Research subjects
Clarification of the clinical conditions for treatment of anti-aquaporin
4 antibody-positive optic neuritis
Development of new imaging diagnostics for optic nerve disease
Evaluation of transcorneal electrical stimulation treatment for optic nerve
diseases
3-4.Strabismic Amblyopia Group
Research subjects
Changes in the cerebral cortex ultrastructure in amblyopia
Clarification of clinical conditions for the treatment of specific types
of accommodative esotropia
3-5.Cornea/Infection Group
Research subjects
Research on epidemiological studies on uveitis
Research on the therapeutic efficacy of biological products for uveitis
Research on surgical results of corneal transplantation
3-6.Ophthalmic Tumor/Ophthalmic Plastic Group
Research subjects
Research on the development of BRAF (V600E) in ocular malignant melanoma
Research on serological and histopathological examinations of patients
with ocular lymphoproliferative diseases and malignant lymphoma meeting
the diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related disease
4.Research Results
|
[Area] Ophthalmology and visual sciences (glaucoma) |
|
|
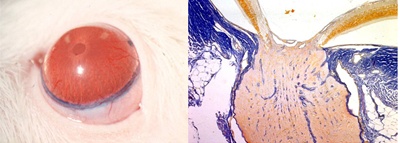
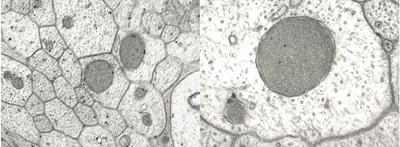
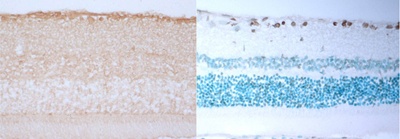
[Research subject] Research on morphological defects of the axonal mitochondria in the optic disc in experimental glaucoma |
|
|
[Description] |
[Photographs]
Creation of a rat glaucoma model (microscopy)
Altered mitochondria scattered in the axon (electron microscopy)
Immunostaining of Caspase 3 in retinal tissue, TUNEL staining finding |
|
[Area] Ophthalmology and visual sciences (neurophthalmology/strabismic amblyopia) |
|
|
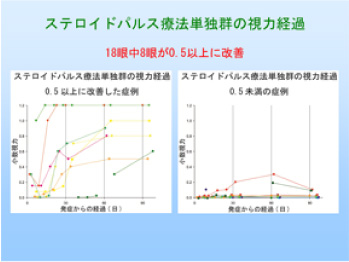
[Research subject] Clarification of clinical conditions for the treatment of anti-aquaporin 4 antibody-positive optic neuritis |
|
|
[Description] |
[Photographs]
|
|
[Area] Ophthalmology and visual sciences (ophthalmic tumor/ophthalmic plastic) |
|
|
[Research subject] Research on the development of BRAF (V600E) in ocular malignant melanoma |
|
|
[Description] |
Please see the Ophthalmology website for a detailed description of our research.