2024年5月14日 抗インフルエンザ剤感受性低下株調査の結果
結果の概要
2024年5月14日時点
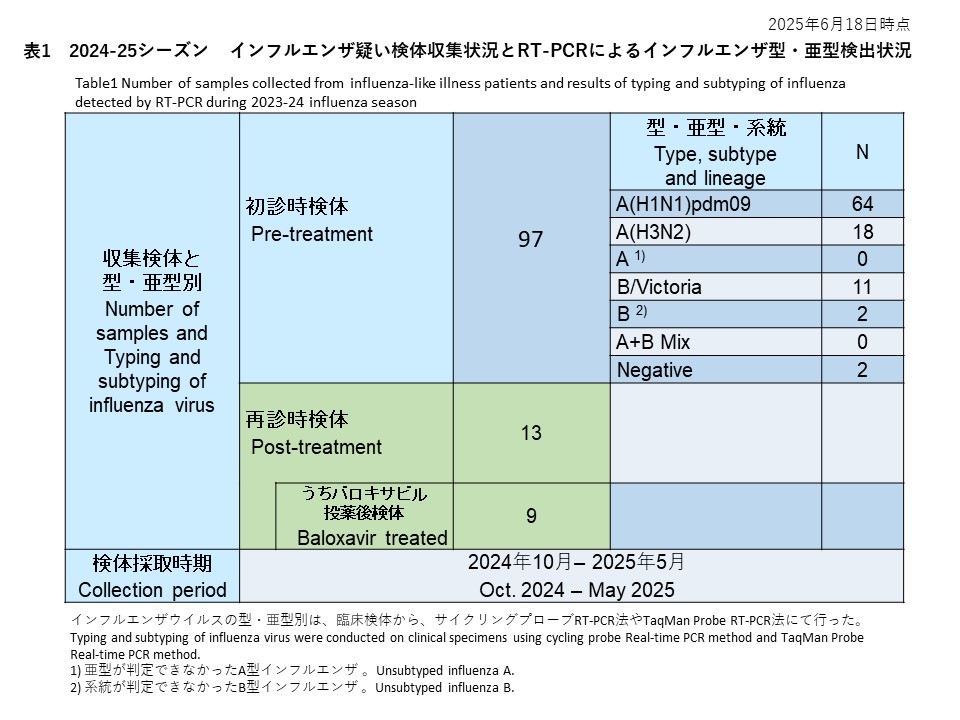
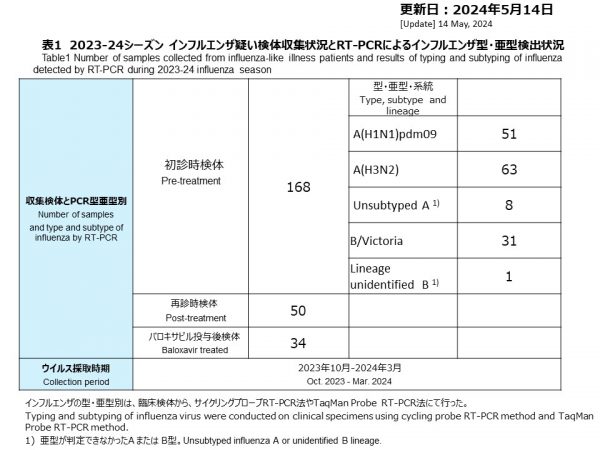
2023年10月から2024年3月にかけて、合計168件の初診時検体が採取されました。再診時検体は50件採取され、うち34件はバロキサビル投与後に採取されました(表1)。
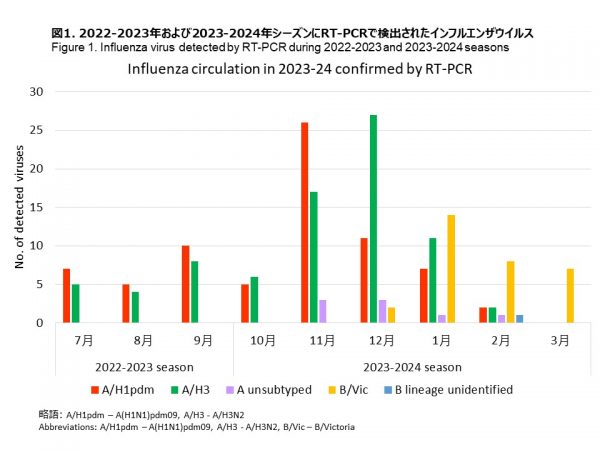
2023年10月以降、インフルエンザA(H1N1)pdm09を51件、A(H3N2)を63件、インフルエンザA型(亜型が特定不能)を8件、B/ビクトリアを31件、インフルエンザB型(系統が特定不能)を1件検出しました(表1,図1)。今シーズンは8月頃からA(H1N1)pdm09とA(H3N2)が同時流行し、11月から12月にピークとなりました。その後A型が減少するとともに、1月からB/ビクトリアが増加し、2月以降はB型が主流となりました。
インフルエンザウイルスのPA蛋白38位がイソロイシンからスレオニンに変異したウイルス(PA/I38T変異株)は、バロキサビルに対して感受性低下を示すと言われています。このPA/I38T変異株を特異的に検出するリアルタイムPCR法(サイクリンブプローブ法)を採取された検体全てに実施しました。
リアルタイムPCR法により、PA/I38T変異を検出したところ、抗インフルエンザ薬投与前のA(H1N1)pdm09の51株、A(H3N2)の63株、B型の31株のいずれにおいてもPA/I38T変異は検出されませんでした(表2)。
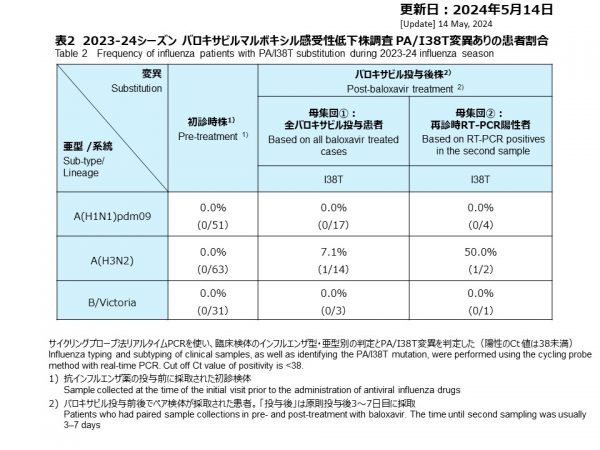
バロキサビル投与後に採取された検体数は34件でした(再診時検体)(表2)。このうち17件がA(H1N1)pdm09で、うち4件がリアルタイムPCR陽性でしたが、PA/I38T変異は検出されませんでした。A(H3N2)は14件から検出され、2件がPCR陽性で、うち1件にPA/I38T変異が検出されました。バロキサビルによる治療後の PA/I38T の出現頻度は、治療症例数を母数とすると 7.1% (1/14) でした。再診時2回目に採取された検体で、リアルタイムPCR法が陽性と確認された検体を母数とした場合、頻度は 50.0% に増加しました。B/Victoriaは2件でしたが、再診時のリアルタイムPCRの結果は全て陰性でした。
[PA遺伝子解析]
次世代シークエンシング(NGS)を用いて解析できた初診時検体52件は、A(H1N1)pdm09が23件、A(H3N2)が28件、B型が1件で、バロキサビルに対する感受性低下を示すと報告されたPA変異はすべての検体にありませんでした。
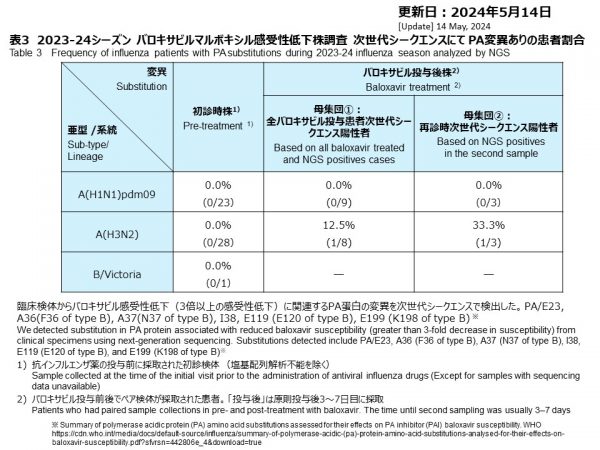
バロキサビル投与後に採取された検体(再診時検体)で、A(H1N1)pdm09の3件とA(H3N2)の3件を、NGSにより解析することができました。A(H1N1)pdm09にはバロキサビルに対する感受性低下を示すと報告された変異は検出されませんでした(0.0%, 0/3)。A(H3N2)の1件にPA/I38T変異が検出されました。バロキサビル治療症例数を母数とすると、この出現頻度は12.5%でしたが(1/8)、NGSによる解析を行うことができた再診時検体数を母数とすると、出現頻度は33.3%に増加しました(1/3)。(表3)。
[NA遺伝子解析]
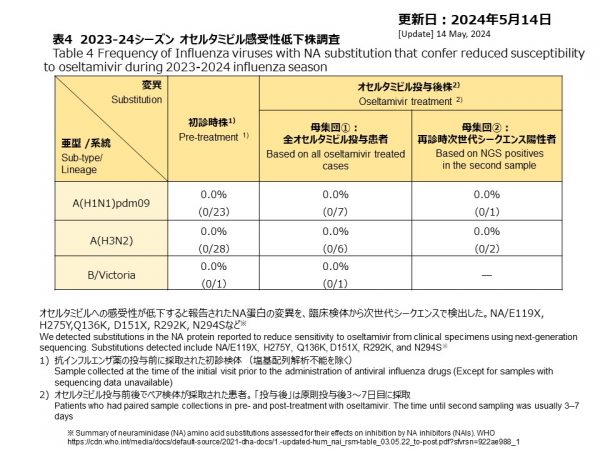
NGSにより解析することができた検体について、同様にオセルタミビルを含むノイラミニダーゼ阻害剤(NA阻害剤)に対する感受性低下を示すと報告されたNA遺伝子の変異についても確認を行いました。初診時に採取された52検体と、治療前後のペア検体採取例でオセルタミビル投与前に採取されたA(H1N1)pdm09の7件、A(H3N2)の6件、B型の1件には、NA阻害剤に対する感受性を低下させる変異はNA遺伝子に検出されませんでした。オセルタミビル投与後検体3件にも検出されませんでした(表4)。
Summary of Results.
As of May 14, 2024
From October 2023 to March 2024, a total of 168 initial visit specimens were collected. There were 50 specimens collected at follow-up visits (second visits), of which 34 were collected after administration of baloxavir (Table 1).
Since October 2023, 51 cases of Influenza A(H1N1)pdm09, 63 cases of A(H3N2), 8 cases of Influenza A (subtype unidentified), 31 cases of B/Victoria, and 1 case of lineage unidentified B were detected (Table 1 and Figure 1). During this season, A(H1N1)pdm09 and A(H3N2) were simultaneously prevalent from around August, with a peak in November and December. Type A subsequently declined, B/Victoria increased from January, and type B became the mainstay of the epidemic from February onward.
A virus with a substitution at position 38 of the PA protein, from isoleucine to threonine (PA/I38T mutation), is reported to confer reduced sensitivity to baloxavir. We implemented a real-time PCR method (cycling probe method) specifically designed to detect this PA/I38T mutation on all samples.
None of the 51 of A(H1N1)pdm09, 63 of A(H3N2), and 31 of influenza B/Victoria samples collected before administration of antiviral influenza drugs showed the presence of the PA/I38T mutation by real-time PCR (Table 2).
There were 34 specimens collected after administration of baloxavir (follow-up visit specimens) (Table 2). Of these, 17 were A(H1N1)pdm09, of which 4 were PCR positive, but the PA/I38T substitution was not detected. There were 14 cases of A(H3N2), two were PCR positive, one of them was PA/I38T positive. The frequency of PA/I38T appearance after treatment with baloxavir was 7.1% based on the number of treated cases (1/14). The frequency increases to 50.0% when based on cycling probe real-time PCR positives in the second samples (1/2). There were two B/Victoria cases, which were PCR negative at the 2nd visit.
[PA Gene Analysis]
Fifty-two initial visit specimens were able to be analyzed using next-generation sequencing (NGS), with 23 cases of A(H1N1)pdm09, 28 case of A(H3N2), and 1 case of type B. None of first visit specimen had any PA substitution, with reduced susceptibility to baloxavir.
Among post-baloxavir-treated cases, 3 influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 and 3 A(H3N2) samples were successfully analyzed by NGS. No PA variants were found among A(H1N1)pdm09 strains (0.0%, 0/3). One influenza A(H3N2)-infected, post-baloxavir-treated case with PA/I38T substitution was confirmed in the PA protein by NGS. The frequency of PA variant appearance analyzed by NGS after treatment with baloxavir was 12.5 % based on the number of treated cases (1/8). The frequency increases to 33.3 % when based on the samples that could be analyzed by NGS in the second samples (1/3) (Table 3).
[NA Gene Analysis]
The same 52 strains successfully sequenced by NGS were analyzed for NA substitutions, affecting sensitivity to neuraminidase inhibitors (NAIs). NGS results showed no substitution in the NA gene affecting sensitivity to NAIs in the 52 prior to treatment cases, which included 7 A(H1N1)pdm09, 6 A(H3N2) and 1 B/Victoria (Table 4). Three post-oseltamivir-treated samples were sequenced and no any NA variants inhibiting NAIs was confirmed (Table 4).