本邦における2021/2022年シーズンの抗インフルエンザ剤感受性低下株調査の結果
2021/22年シーズン 抗インフルエンザ剤感受性低下株調査の結果
新潟大学大学院医歯学総合研究科・国際保健
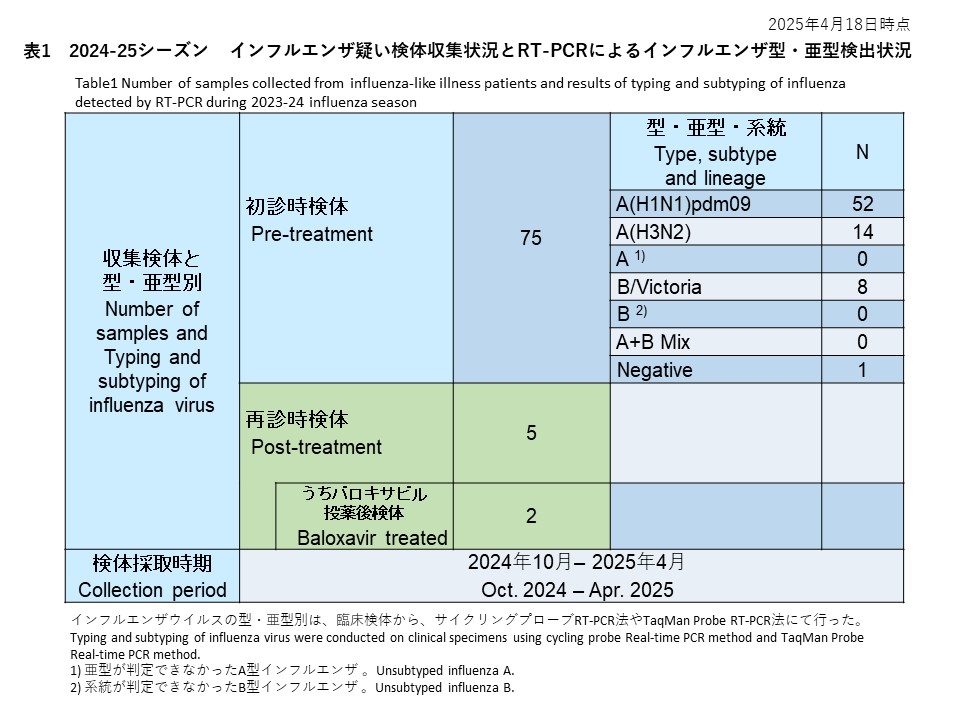
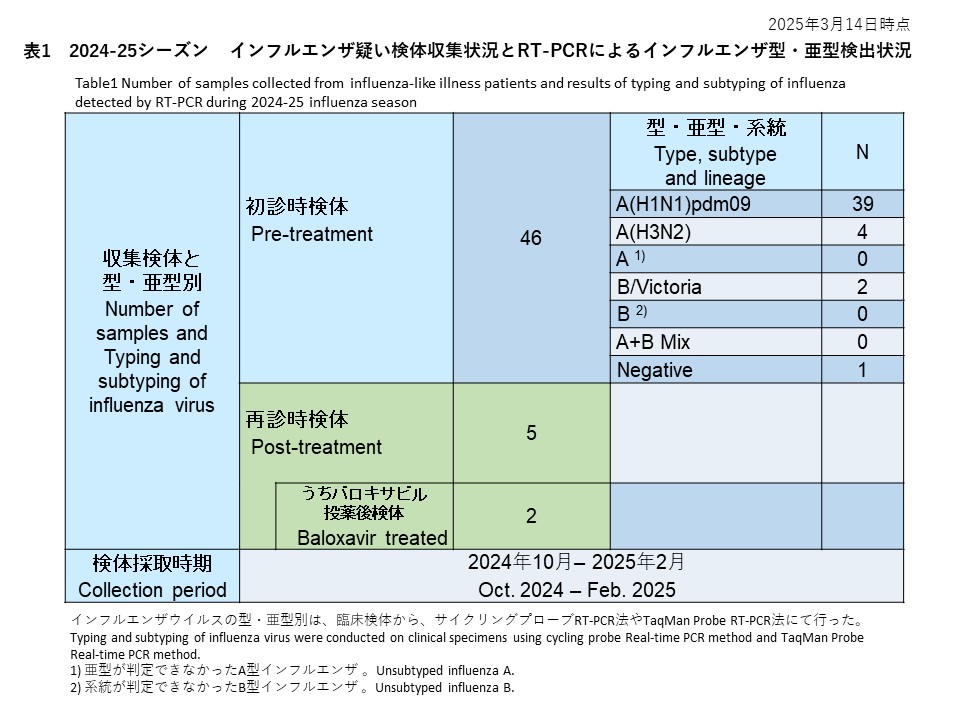
概要:2021/22年シーズンに検出されたA/H3N2の4件はいずれも抗インフルエンザ剤感受性低下はなく、バロキサビルとノイラミニダーゼ阻害剤に対して感受性であると考えられました。
2021/2022年のインフルエンザ抗インフルエンザ剤感受性低下株調査の結果を報告します
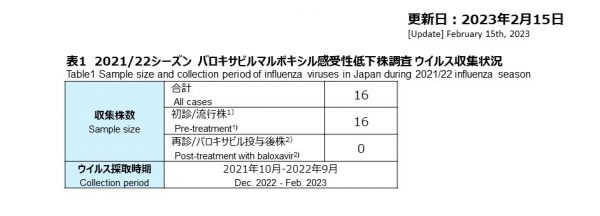
2021年10月から2022年9月末まで、全国14医療施設に依頼し、合計16件のインフルエンザ疑いの検体を受領しました。抗インフルエンザ約初診時検体のみで再診検体は採取できませんでした。リアルタイム PCRで、まず新型コロナウイルスのスクリーニングし、その後、リアルタイム PCR とウイルス培養を使ってインフルエンザを検出しました。結果として、A型インフルエンザ4件(4/16, 25%)を検出し、いずれもA/H3N2でした。A/H1N1pdm09やB 型インフルエンザは検出されませんでした。
時期的には、2022年1月から3月にかけて採取された12件中、7件より新型コロナウイルスが検出されました。2022年7月から8月初めに採集された4検体は、4件全てよりインフルエンザA/H3N2が検出されました。
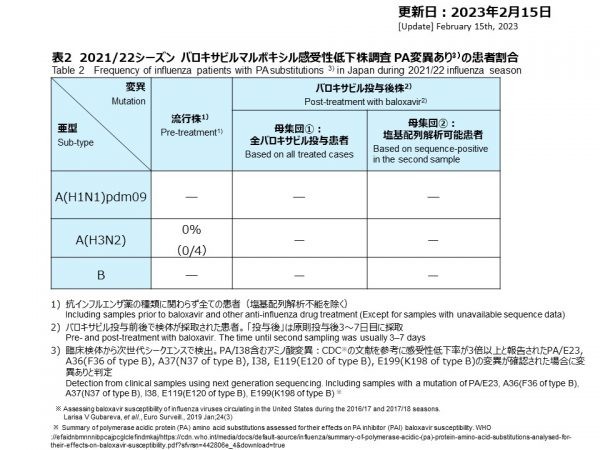
A/H3N2と判定された、4件について臨床検体から次世代シークエンスを実施し、ウイルス全シークエンス解析を行いました。PA遺伝子には、バロキサビルに対して感受性低下を起こす変異(PA/E23K, PA/I38Xなど)は、4件とも認められなかったため、バロキサビルに対して感受性であると考えられました。NA遺伝子には、ノイラミニダーゼ阻害剤に対してA/H3N2で感受性低下を起こす変異(NA/Q136K, NA/N294S, NA/R292Kなど)は、4件とも認められなかったため、ノイラミニダーゼ阻害剤に対しても感受性であると考えられました。
結果的に、当該シーズンの抗インフルエンザ剤感受性低下株の検出数はバロキサビル、ノイラミニダーゼ阻害剤共に0.0%(0/4)でした。
HA遺伝子の解析の結果、この4件のウイルスはWHOクレード3C.2a1b.2a.2に属し、2022/23年北半球ワクチン株A/Darwin/6/2021と遺伝子的に近縁のウイルスでした。2022年8月頃にオーストラリアで流行したウイルスとも非常に近いHA遺伝子配列を持っていました。
Abstract: Four A/H3N2 detected during the 2021/22 season were all susceptible to anti-influenza drugs, baloxavir and neuraminidase inhibitors.
Results of the 2021/2022 Influenza Anti-Influenza Drug Susceptibility Investigation conducted by Division of International Health, Niigata University are reported.
From October 2021 to the end of September 2022, 14 medical facilities nationwide participated to the study, we and received a total of 16 samples from influenza-like illness patients. Only pre-treatment samples were collected and no second visit samples after treatment were received.Firstly SARS-CoV-2 was screened by Real-time PCR, and then influenza was detected using real-time PCR and viral isolation.As a result, four cases of influenza A (4/16, 25%) were detected, all of which were A/H3N2.No influenza A/H1N1pdm09 or B was detected.
SARS-CoV-2 were detected in 7 of the 12 cases collected from January to March 2022.Four samples collected from July to early August 2022 turned out to be influenza A/H3N2.
Next-generation sequencing was performed on the clinical specimens from the four cases that were determined to be A/H3N2, and a whole-virus sequencing analysis was implemented.No substitutions in polymerase gene (PA/E23K, PA/I38X, etc.) causing decreased susceptibility to baloxavir were found in any of the four A/H3N2 viruses, suggesting that they were susceptible to baloxavir.No substations in neuraminidase gene (NA/Q136K, NA/N294S, NA/R292K, etc.) causing decreased susceptibility to neuraminidase inhibitors were not observed in any of the four A/H3N2 viruses, suggesting that they are also susceptible to neuraminidase inhibitors.
As a result, the number of viruses that confer reduced susceptibility was 0.0% (0/4) for both baloxavir and neuraminidase inhibitors.
HA gene analysis showed that the four A/H3N2 viruses belonged to WHO clade 3C.2a1b.2a.2 and were genetically related to the 2022/23 Northern Hemisphere vaccine strain A/Darwin/6/2021. They are also very similar to the viruses that circulated in Australia around August 2022.